Certificate Overview
With an SSL/TLS certificate you can encrypt the data traffic between web server and client and protect it from misuse. Especially for applications where sensitive data is sent over the internet, e.g. online shops, an SSL/TLS certificate is essential.
KeyHelp offers you the possibility to store already existing certificates, to create a certificate request in order to request a certificate from a certificate authority, or to create a self-signed certificate.
The web server supports SNI (Server Name Indication). It is therefore no longer necessary to assign an IP address to domains for which a certificate should be used. Any number of SSL/TLS domains can be configured on one IP.
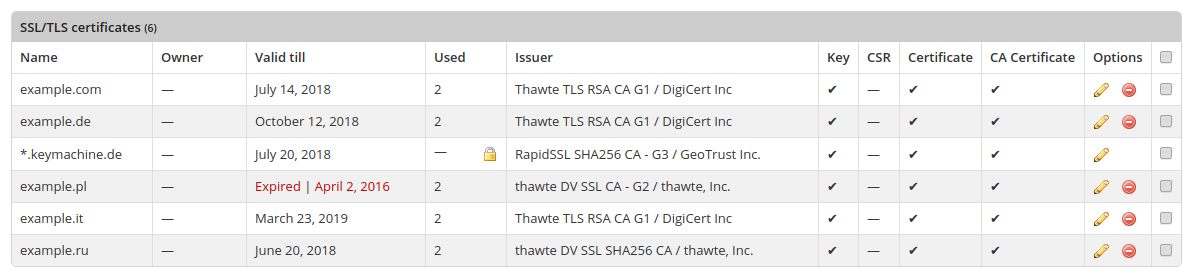
After opening the menu item, the SSL/TLS certificates available on the server are displayed in a table.
To add a new certificate, click the button:
To delete one or more selected certificates, click the button:
To secure server services with a certificate ( Specify Certificates for Server Services ), click:
Meanings of Icons & Column Captions
|
Name |
The name of the certificate. |
|
Owner |
The user name of the KeyHelp user to which the certificate has been assigned. |
|
Valid till |
Displays the date until the certificate is valid. |
|
Used |
Shows the number of domains for which the certificate has been activated. |
|
Issuer |
Displays the name of the certification authority that issued the certificate. |
|
Key |
Shows whether a private key has been stored for the certificate. Each certificate consists of a key pair with a public and a private key. The private key with the code and the public key for decoding. |
|
CSR |
Shows whether a CSR (Certificate Signing Request) has been stored for the certificate. CSR is a public key. The CSR is required when applying for the certificate because it verifies certain information about the web server and your company. For the function of a certificate it is not necessary that a CSR is stored. |
|
Certificate |
Shows whether the actual certificate has been stored. The certificate is the electronic ID of the website, which confirms its identity. |
|
CA-Certificate |
Shows whether the certificate of the certificate authority has been stored. Normally, these root and intermediate certificates of trusted issuers are already integrated in the browsers. To avoid problems with certain browsers, it is recommended to store the CA certificate. |
| |
The certificate is used to protect one or more server services (FTP / Email /...). |
| |
Opens the corresponding certificate for editing. |
| |
Deletes the corresponding certificate. A confirmation prompt appears. |



